Colorful Diffuse Intrinsic Image Decomposition in the Wild
Best Paper Award Honorable Mention
Patent pending
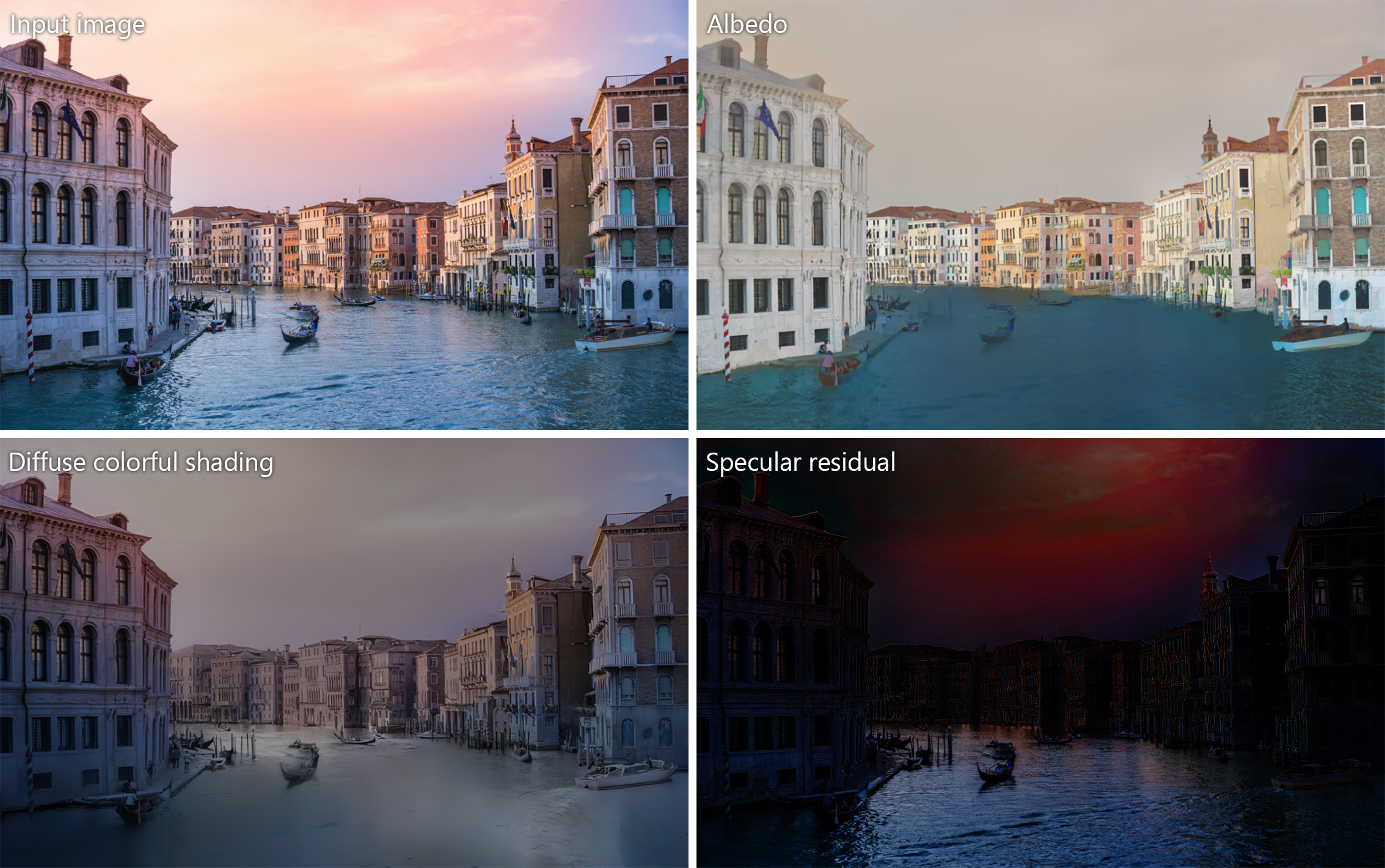

We present a method that can represent in-the-wild photographs in terms of albedo, diffuse shading, and non-diffuse residual components. Our shading layer reflects the colorful nature of multiple illuminants and secondary reflections in the scene, while our residual layer models the specularities and visible light sources.
Abstract
Intrinsic image decomposition aims to separate the surface reflectance and the effects from the illumination given a single photograph. Due to the complexity of the problem, most prior works assume a single-color illumination and a Lambertian world, which limits their use in illumination-aware image editing applications. In this work, we separate an input image into its diffuse albedo, colorful diffuse shading, and specular residual components. We arrive at our result by gradually removing first the single-color illumination and then the Lambertian-world assumptions. We show that by dividing the problem into easier sub-problems, in-the-wild colorful diffuse shading estimation can be achieved despite the limited ground-truth datasets. Our extended intrinsic model enables illumination-aware analysis of photographs and can be used for image editing applications such as specularity removal and per-pixel white balancing.
Implementation
Paper
 |
 |
BibTeX
author={Chris Careaga and Ya\u{g}{\i}z Aksoy},
title={Colorful Diffuse Intrinsic Image Decomposition in the Wild},
journal={ACM Trans. Graph.},
year={2024},
volume = {43},
number = {6},
articleno = {178},
numpages = {12},
}
License
The methodology presented in this work is safeguarded under intellectual property protection. For inquiries regarding licensing opportunities, kindly reach out to SFU Technology Licensing Office <tlo_dir ατ sfu δøτ ca> and Dr. Yağız Aksoy <yagiz ατ sfu δøτ ca>.
Chris receiving his award at SIGGRAPH Asia 2024
 |
Related Publications